- Home
- Resources
- Phenotyping
- PhenoSense Entry
Monogram Biosciences

PhenoSense® Entry
PhenoSense® Entry provides a direct and quantitative measurement of how a patient's virus responds to enfuvirtide (FUZEON®).
PhenoSense® Entry assesses resistance to enfuvirtide, which interacts with glycoprotein gp41 of the HIV envelope. The test also assesses resistance to entry inhibitors that interact with gp120 (eg, chemokine receptor antagonists, attachment inhibitors) and is used in their clinical development. It is used for assessing resistance to current and future entry inhibitors.
Alternative approaches may not account for the high genetic heterogeneity observed in this part of the virus.
PhenoSense® Entry is a commercially available test for testing resistance to entry inhibitors. The assay assesses resistance to enfuvirtide, which interacts with glycoprotein gp41 of the HIV envelope.
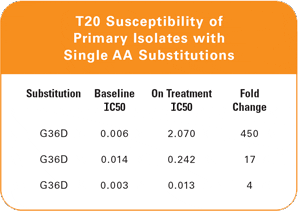
Genotyping may be insufficient because data have shown that areas outside of the envelope impact enfuvirtide susceptibility. This may explain why a wide range of fold changes† has been observed with similar mutational patterns.
Together with PhenoSense® GT, a combination phenotype and genotype drug resistance test, and PhenoSense® Integrase, PhenoSense® Entry provides the most complete picture of resistance to antiretroviral medications2.

